How DC/DC power efficiencies are meeting 5G challenges

Today’s wireless networks are struggling to keep up with the world’s insatiable hunger for more data, fueled by innovations such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous cars and virtual reality. In response, new 5G technology promises to enable countless new applications, leading to exponential growth in transported data and a need for many more base stations and data centers. China is the frontrunner in 5G, with 460 million 5G connections expected by 2025, and the first 5G sites live already.
Some analysts predict that data rates will reach almost 107 exabytes (EB) per month by the end of 2023 (39% CAGR). With estimates that 5 kWh is currently needed to support the utilization of every GB of internet data, it’s clear that 5G power consumption will need to significantly decrease – if the technology is to be both environmentally sustainable and economically viable.

Problems for operators and data center owners
The 5G rollout will bring new challenges to network and data center operators. Within the network, the massive connectivity demands of IoT devices, and other applications, along with the short range of mmWave signals, will drive a huge increase in the number of base stations. Additionally, with massive MIMO technology, 5G base stations will have up to 64 transmitters. Without any efficiency measures, the 300 Watt input power requirement of a typical 4G base station radio unit will increase to 1100 to 1500 Watts for 5G.
With base stations already accounting for 60% of total network power consumption, and operators’ energy costs estimated to be 15% of operating expenditure, this is unsustainable, and innovative efficiency measures are needed. For example, designers of the Radio Frequency Power Amplifier (RFPA), one of the most power-hungry components, are increasingly moving from LDMOS to Gallium Nitride (GaN) transistors, thus increasing the efficiency of the power amplifier. Another key RFPA design technique is Envelope Tracking/Restoration (ET/ER), but this requires a very efficient DC-DC converter.
In the data centre, increased processing power and storage capacity will be needed, meaning more servers, racks, power, cooling and space. Network and data center operators therefore face twin challenges of packing more functionality into smaller spaces and decreasing energy consumption.
Power supplies meet the technical challenge
New developments in power management and DC conversion techniques are helping solve this issue. They have transformed systems design, enabling more efficient and compact servers and other electronic equipment.
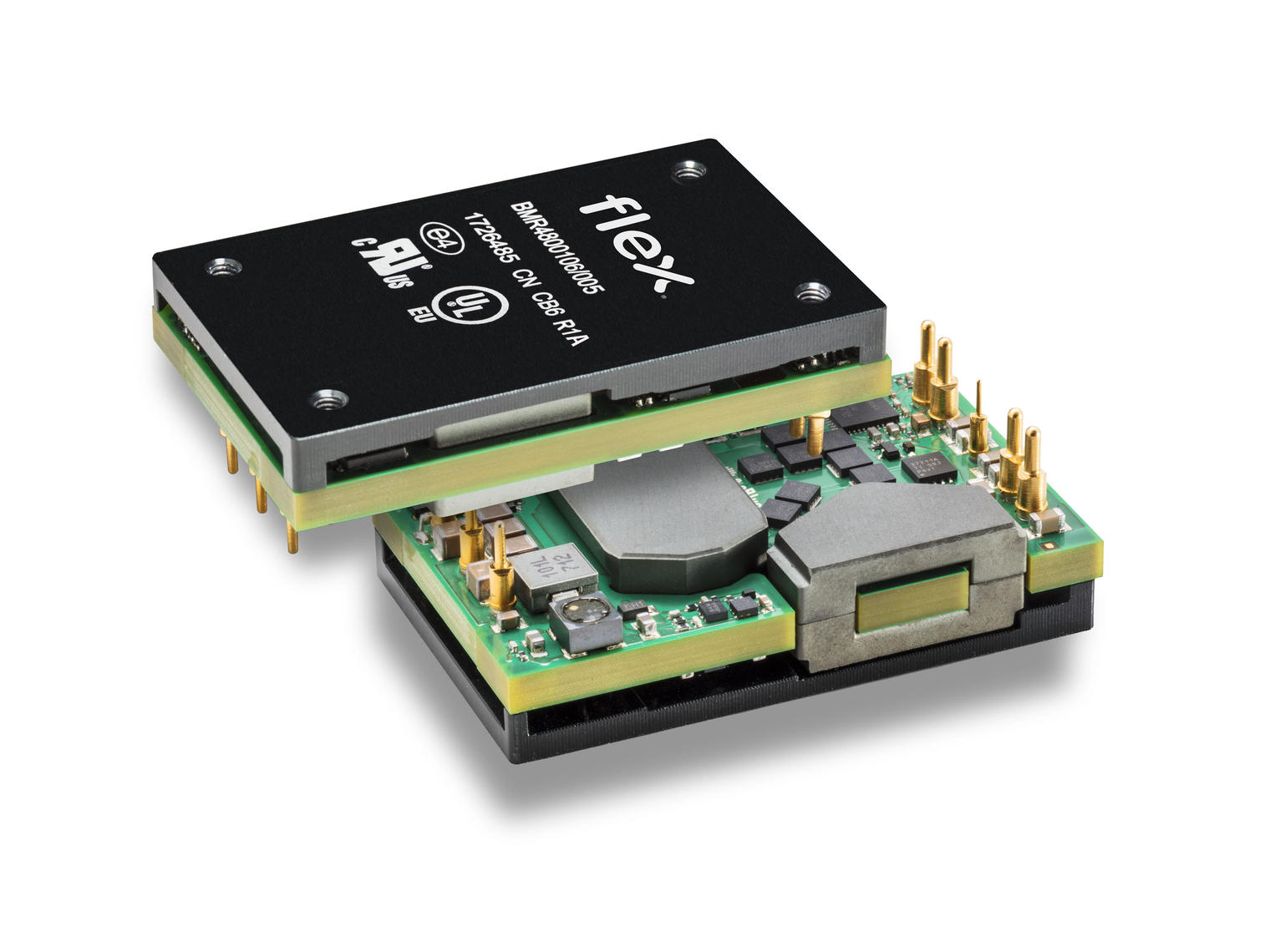
Firstly, digital power ICs (Figure 1) combine the benefits of both digital communications and modular DC/DC solutions, enabling system designers to develop more compact and efficient products with small form factors.
Time to market for new product development is shortened as designers can take advantage of the functionality within the power modules plus a range of support tools, freeing themselves from complex power supply design.
Figure 1: Flex Power Modules’ BMR480 Digital DC/DC Module

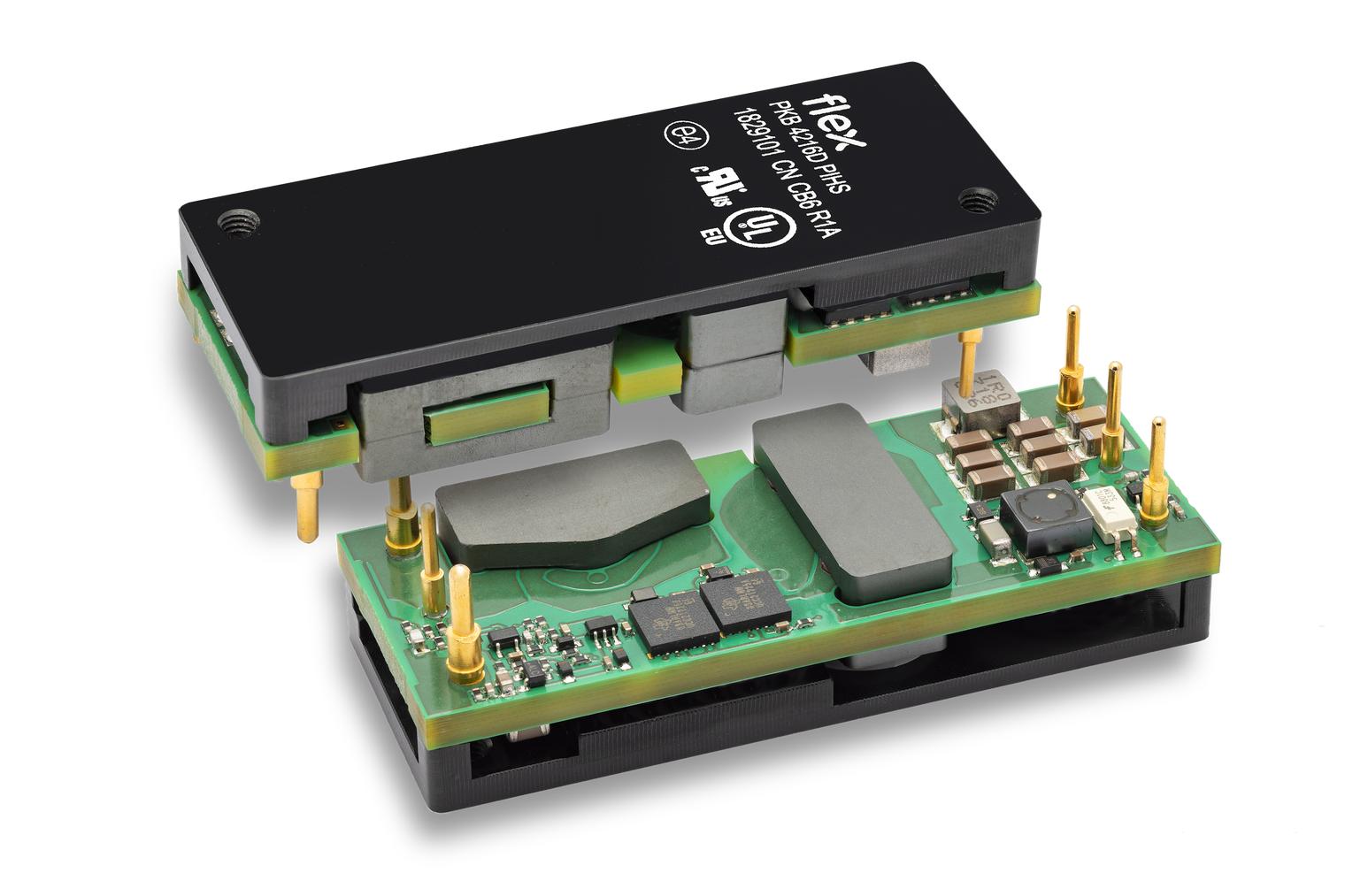
For powering RFPAs, analog DC/DC converters continue to improve, with innovations that are improving density, integration, reliability and efficiency. For example, Flex Power Modules’ PKB4216HDPI is a 250W rated DC/DC converter in the eighth-brick format, which is suitable for powering 50V GaN-based RFPAs as well as high voltage LDMOS RFPA applications. For higher-power RFPAs, the PKJ4000 series delivers up to 700W at 28V or 50V DC.
Figure 2: Flex Power Modules' PKB4216D
Customers rely on greater choice, quality and support
Following the recent acquisition of Ericsson Power Modules, Flex Power Modules has a track record of over 40 years in supplying power solutions for telecommunications and data centers. In China, the company's Shanghai site has 350 employees focused on delivering high quality technology that meets global standards, with mass production capabilities and the agility required to supply changing market demands.
Flex’s portfolio includes a wide range of isolated DC/DC converters and non-isolated point-of-load (PoL) converters, and also power interface modules (PIM) for ATCA applications, such as processor and switch blades. Its isolated DC/DC power products offer ultra-high efficiencies, currently up to 98%, extremely high reliability, configuration and control capabilities via PMBus, and compact formats down to sixteenth-brick size.
Flex’s leading-edge design tools include its Flex Power Designer software. This enables designers to run detailed simulations including thermal modelling, minimizing power system design errors and reducing development time – and hence cutting time-to-market.
Conclusion
The sustainability and economic viability of 5G networks and data centers increasingly depend upon advanced digital power supply techniques. Flex Power Modules is the world’s leading provider of digital power supply solutions with an end-to-end product portfolio which includes PIM, isolated brick and digital POL modules, as well as a growing range of analog RFPA-specific products to support LDMOS and GAN based designs. As well as improving efficiency, Flex’s wide portfolio enables developers to reduce design cycles and increase speed to market with innovative network and data center equipment.
Our range of products suitable for 5G / RFPA applications can be seen HERE
