Thermal management and cooling techniques

Thermal design for DC/DC converters is a critical aspect of ensuring the reliability and longevity of power electronics systems. DC/DC converters generate heat due to switching and conduction power losses in the components (such as semiconductors, inductors, and capacitors) during the power conversion process.
Effective thermal management is necessary to prevent overheating, which can degrade the performance of the converter and cause component failure.
Thermal management
To manage the heat generated in DC/DC converters, several techniques are used, including:
- Forced air cooling using heatsinks: Adding heat sinks to power components, especially the power transistors, can greatly improve thermal dissipation. The heatsink's surface area and thermal conductivity are key factors, alongside the rate of flow of cooling air.
- Direct to Chip liquid cooling: Liquid cooling systems typically involve circulating a coolant (water or a dielectric fluid) through a closed-loop system that removes heat from the DC/DC converter and dissipates it in a radiator or heat exchanger. More information on this technology can be found on JetCool's website - https://jetcool.com/ - which is a Flex company.
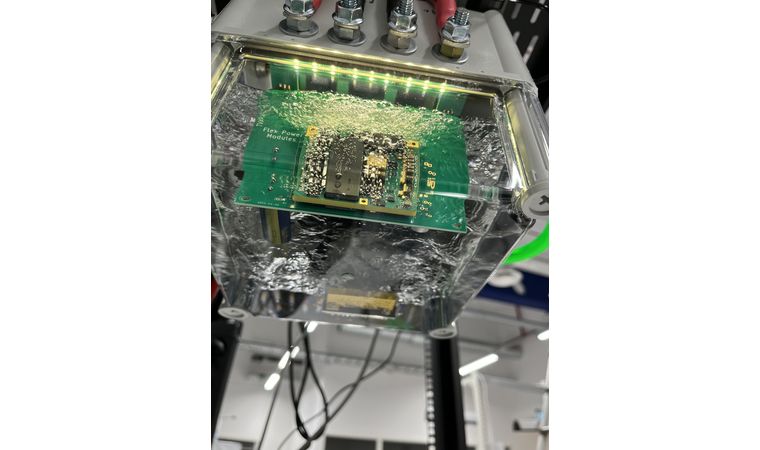
- Immersive cooling: This is an advanced thermal management technology used to cool electronic components by submerging them directly in a specially designed coolant or dielectric fluid. These fluids do not conduct electricity but are highly effective at transferring heat. There are two main forms of immersive cooling – single phase, where the cooling fluid maintains its liquid state, and two phase, where the liquid boils and changes state to a gas before condensing back to a liquid.
JetCool, a Flex company, offers direct-to-chip liquid cooling modules that use arrays of small fluid jets that precisely target hot spots on processors, transforming high-power electronic cooling performance at the chip or device level. More information can be found at https://jetcool.com/
Please also take a look at some of the additional resources we offer below:
Featured Content
With the enormous power levels seen in latest AI-targeted processors, liquid cooling has become a necessity.

Liquid cooling is increasingly vital in AI data centers as traditional methods struggle to keep manage intense heat.

Cooling processors in data centers is a major technical and cost issue that could be a bottleneck to further performance gains. We look at the challenge and ask if it might limit the potential of applications such as AI.
The power ratings and conversion efficiency of voltage regulator modules are increasing, but expected size is reducing and as a result, effective heat dissipation remains a design challenge. This blog considers some cooling options in products available from Flex Power Modules.
Immersive cooling has been around for many years in demanding applications and is now becoming attractive in commericial and industrial applications. There is a natural concern about the compatibility of the available fluids with the materials used in mass-produced products such as DC/DC converters.
